Relative aperture, the measure of the light-gathering power of an optical system. … For binoculars, telescopes, and photographic lenses in which the object may be distant, the relative aperture is taken as the ratio of focal length of the objective to the diameter of the entrance pupil.
Also, IS F 4.0 A large aperture?
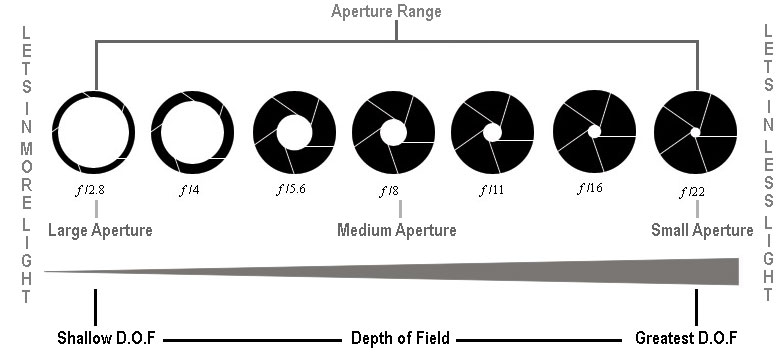
Minimum and Maximum Aperture of Lenses
A lens that has a maximum aperture of f/1.4 or f/1.8 is considered to be a “fast” lens, because it can pass through more light than, for example, a lens with a “slow” maximum aperture of f/4.0. That’s why lenses with large apertures usually cost more.
Beside above What is meant by circle of confusion? In optics, a circle of confusion is an optical spot caused by a cone of light rays from a lens not coming to a perfect focus when imaging a point source. … In photography, the circle of confusion (CoC) is used to determine the depth of field, the part of an image that is acceptably sharp.
What is depth camera?
For many cameras, depth of field (DOF) is the distance between the nearest and the farthest objects that are in acceptably sharp focus in an image. The depth of field can be calculated based on focal length, distance to subject, the acceptable circle of confusion size, and aperture.
Which f-stop is sharpest?
The sharpest aperture of your lens, known as the sweet spot, is located two to three f/stops from the widest aperture. Therefore, the sharpest aperture on my 16-35mm f/4 is between f/8 and f/11. A faster lens, such as the 14-24mm f/2.8, has a sweet spot between f/5.6 and f/8.
Is f-stop shutter speed?
F/stop exercise. Keep in mind that f/stops, shutter speeds and film/digital sensor speeds are nearly always related by precisely half or double. That is, changing your f/stop from, say, 4 to 5.6 (one stop) is the same as changing your shutter speed from 125 to 250. Each lets in half as much light.
How do you use the circle of confusion?
By simply adjusting focal length and f-stop numbers, you can adjust the circle of confusion on your image plane without performing a single mathematical calculation, thus achieving sharper focus. Circle of confusion values do come in handy when you use depth of field charts (DoF charts).
What are f stops in photography?
An f–stop is a camera setting that specifies the aperture of the lens on a particular photograph. It is represented using f-numbers. The letter “f” stands for focal length of the lens.
How do you find the circle of least confusion?
Spherical Equivalent = Sphere + Cylinder / 2
For example, given a prescription of +2.00 DS -1.00 DC 180, the spherical equivalent (and the location of the circle of least confusion) is given by +2.00 + (-1.00) / 2 = +1.50 D, or 66.7 cm behind the lens.
What are the two types of depth of field?
There are two types of DoF, the first being shallow and second being narrow. Shallow DoF being Apertures below F2. 8, typically. And more narrow DoF being Apertures greater than F8.
Does ISO affect depth of field?
ISO settings can be used to compensate for your bigger or smaller aperture preference and so can shutter speeds, but they do not directly affect Depth Of Field.
When would you use depth of field?
Depth of field is the area of acceptable sharpness in front of and behind the subject which the lens is focused. Put simply, it refers to how blurry or sharp the area is around your subject. A shallow depth of field refers to a small area in focus. Often the subject is in focus, while the background is blurred.
Is 1.8 or 2.2 aperture better?
A 50 mm f/1.8 lens has an aperture diameter of 50/1.8 = 27.78 mm diameter. f/2.2 is likely a better quality lens (less aberrations, a wide aperture becomes difficult), and is smaller, lighter, and less expensive, but f/1.8 opens wider to see more light in a dim situation.
What does f 2.8 mean in photography?
Here’s the aperture scale. Each step down lets in half as much light: f/1.4 (very large opening of your aperture blades, lets in a lot of light) f/2.0 (lets in half as much light as f/1.4) f/2.8 (lets in half as much light as f/2.0)
How is shutter speed calculated?
So if you are shooting with a 500mm lens, you should set your shutter speed to 1/500 or higher. If you are using a DSLR that has a crop factor you have to multiply by the crop factor. For example most Nikon SLRs has a 1.5 crop factor – for the example above you will to set the shutter speed to 1/(500*1.5) = 1/750.
What is a good shutter speed for portraits?
Shutter Speed
Most professional photographers shoot portraits at a shutter speed of around 1/200 of a second. This is not because of camera shake, generally, but because this is the maximum synch speed of most flash units employed in studio portrait shoots.
What is ISO vs aperture?
Two controls affect the amount of light that comes into the camera and strikes the image sensor – aperture and shutter speed. The ISO affects how much light is needed to produce a correct exposure. The lens aperture is a diaphragm that is in the lens itself or immediately behind it.
What is CA in photography?
In optics, chromatic aberration (CA), also called chromatic distortion and spherochromatism, is a failure of a lens to focus all colors to the same point. … Chromatic aberration manifests itself as “fringes” of color along boundaries that separate dark and bright parts of the image.
What is hyper focus distance?
In optics and photography, hyperfocal distance is a distance beyond which all objects can be brought into an “acceptable” focus. As the hyperfocal distance is the focus distance giving the maximum depth of field, it is the most desirable distance to set the focus of a fixed-focus camera.
What is Sturm’s Conoid?
STURM’S CONOID: It is an optical condition in which refractive power of cornea and lens is not the same in all meridians , therefore instead of single focal point there are two focal points separated by focal interval, this is called sturm’s conoid.
What are blur circles?
The image formed by a lens system, on its focal surface, of a point source object. The size of the blur circle will be dictated by the precision of the lens and the state of focus; i.e., the blur can be caused by aberrations, defocusing and manufacturing defects.
Why do photographers use depth of field?
Depth of field (DoF) is an important concept to understand and can make your photography stand out. A deep depth of field will give you a photograph with near and far objects all in good focus. A shallow depth of field will put the emphasis on just the important of your photo that you want to highlight.
How do you shoot depth of field?
The aperture is the setting that beginners typically use to control depth of field. The wider the aperture (smaller f-number f/1.4 to f/4), the shallower the depth of field. On the contrary, the smaller the aperture (large f-number: f/11 to f/22), the deeper the depth of field.
How do I get good depth of field?
3 Ways to Control Depth of Field
- Adjust your aperture. Use a low f-stop (f2. …
- Change your focus distance. The closer you are to the thing you are focusing on, the less depth of field you’ll have and vice versa. …
- Change the focal length of your lens. Wide lenses (like 16-35mm) give a wider depth of field.




Discussion about this post