What are marketed as “1 inch sensors” are actually only about 9 x 12 millimeters on a good day, or about 0.35 x 0.47″ — nowhere near one inch. These little sensors have only about one-quarter the area of a typical crop-frame DSLR (16x24mm), and only about one-eighth the area of a full-frame (24x36mm) sensor.
Also, How do you calculate sensor width?
Calculating Camera Sensor Width
- in a RED Epic, the pixel pitch is 5.4 µm (or 0.0054mm)
- at “4K 16:9,” the number of pixels actively capturing light is 4096 px by 2304 px (width is 4096 pixels).
- Thus: pixel pitch * horizontal pixel count = Camera Sensor Width. 0.0054 (px/mm) * 4096 (px) ≈ 22.12 (mm)
Beside above Does sensor size really matter? Right off the bat, let’s clear things up by saying yes, all things being equal, a larger sensor will give you a better image file, but like most matters in life, all things are not equal. The common wisdom is that for each jump in sensor size, you gain about a stop of performance in terms of noise and dynamic range.
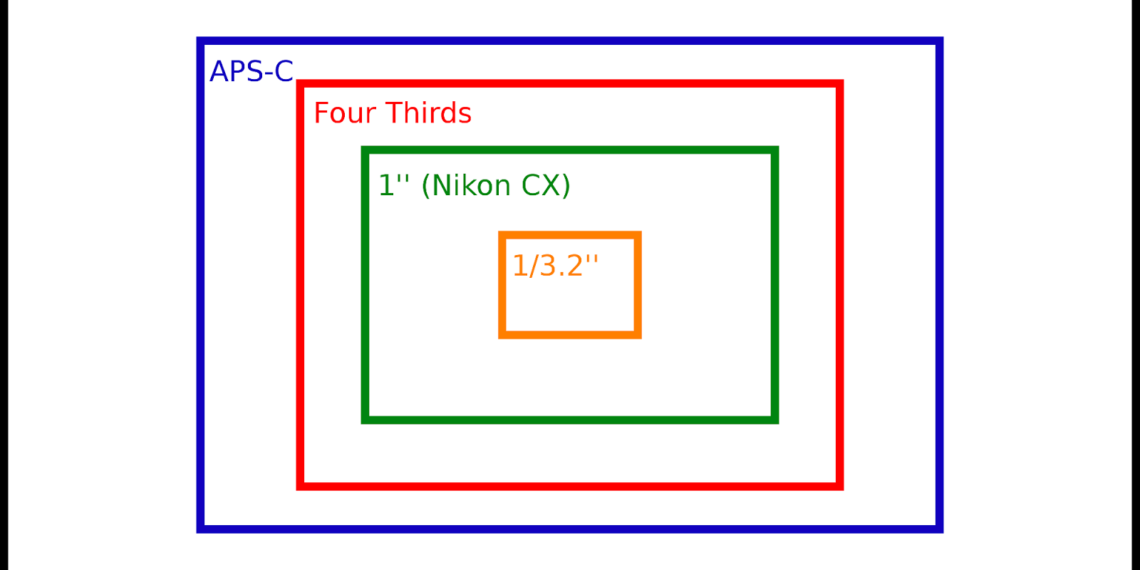
What size is a crop sensor?
These dimensions are 36mm x 24mm. This gives the aspect ratio of 3:2 (three units wide compared to two units tall), which is the ratio most DSLR cameras shoot in. By definition, a crop sensor is anything smaller than these measurements. The most common of these are APS-C and micro four thirds.
Does sensor size affect field of view?
The width and height of the sensor will determine the Field Of View, and will be used to calculate the Crop Factor. FOCAL LENGTH The focal length of a lens will never change, regardless of the sensor used. … The combination of Sensor Size and Focal Length will change the Angle of View and the Field Of View.
How sensor size affect image quality?
The larger your camera’s sensor, the larger the photosites, the more resultant megapixels, which allow for a better image and a higher resolution. High resolution is important to ensure that your images are high quality even when you blow up a photo to a larger size.
Why is a bigger sensor better?
Larger Camera Sensors Have Better Image Quality
Larger camera sensors capture images with more light, less noise, more detail, and more of that beautiful background blur, to name a few. When comparing two cameras, if one has a larger sensor, that one will have better image quality.
Does sensor size affect depth of field?
As sensor size increases, the depth of field will decrease for a given aperture (when filling the frame with a subject of the same size and distance). This is because larger sensors require one to get closer to their subject, or to use a longer focal length in order to fill the frame with that subject.
Is crop sensor better than full frame?
Generally, a full frame sensor can provide a broader dynamic range and better low light/high ISO performance yielding a higher quality image than a crop sensor. … Most lenses made for full-frame systems cost more and weigh more because they are higher quality.
What is sensor crop?
A crop sensor is smaller than the standard 35mm size, which introduces a crop factor to the photos these cameras take. This means that the edges of your photo will be cropped for a tighter field of view.
How does sensor size affect image quality?
The larger your camera’s sensor, the larger the photosites, the more resultant megapixels, which allow for a better image and a higher resolution. High resolution is important to ensure that your images are high quality even when you blow up a photo to a larger size.
Do smaller sensors have more depth of field?
This means that, at the same distance from your subject, at the same physical focal length and aperture setting, a camera with a smaller sensor will have shallower depth of field than the one with a larger sensor.
How does a crop sensor affect the field of view?
When we use 35mm film as a standard, any camera with a sensor smaller than a frame of 35mm film will cover a smaller portion of the image circle produced by a given lens and will thereby change the field of view of that lens. This is the “crop” part of the crop factor.
What size is a full frame sensor?
A full frame digital sensor refers to to the negative size of a 35mm film camera. These dimensions are 36mm x 24mm. This gives the aspect ratio of 3:2 (three units wide compared to two units tall), which is the ratio most DSLR cameras shoot in. By definition, a crop sensor is anything smaller than these measurements.
Does sensor size affect ISO?
Sensor size mostly affects depth of field, light gathering, ISO performance, field of view, and dynamic range. Each of these has an important impact on the final image you create.
Does sensor size affect video quality?
Answer to first question you need about a 9 megapixel sensor to even be able to resolve 4K then you need the video output processorencoder to actually convert that frame data into multiple frames aka “video”. Generally the bigger the sensor the higher the “potential” for quality.
Is there a sensor bigger than full frame?
“Medium format” is generally used to refer to film frames or sensor sizes that are larger than 35mm full frame (24x36mm) but smaller than large format (4x5in). … As you can see, Fuji’s new sensor is noticeably larger than 35mm full frame, but noticeably smaller than Phase One XF medium format cameras.
Does sensor size affect exposure?
F-stop number does not change depending on your sensor size since it’s a ratio based on physical properties of the lens, and instead will, more or less, scale with the change of focal length and size of lens due to change in sensor size. … This means that exposure from aperture is not affected by sensor size.
Do larger sensors gather more light?
A sensor with bigger pixels will collect more light, and more light will generally improve image quality. … Assuming the resolution remains the same between formats, the larger sensor will obviously have bigger pixels and, therefore, will deliver better image quality.
Is a full frame sensor worth it?
Buy a new full frame camera if you have invested in a few good lenses. If you only have kit lenses, then you should not buy a new camera body yet. … If you photograph events that have awful light and won’t allow flash photography, then the ISO performance of a full frame camera is a feature worth paying for.
Is CMOS a crop sensor?
Canon’s 1.3x crop camera bodies are the only DSLRs that use this format. These include the EOS 1D Mark III and Mark IV. SENSOR TYPE: CMOS and CCD are two different technologies used to capture images digitally.
Is full frame sharper than crop?
APS-C sensors: cropped images
With an APS-C sensor, the angle of view is narrower. This creates the impression of being zoomed in more. Although the depth of field remains the same in both cases, the background is “sharper” than the same shot taken with a full frame sensor and the same aperture.
Does sensor size affect image quality?
The larger your camera’s sensor, the larger the photosites, the more resultant megapixels, which allow for a better image and a higher resolution. High resolution is important to ensure that your images are high quality even when you blow up a photo to a larger size.
Does a crop sensor increase magnification?
That means: you’re increasing the magnification of the image from the smaller sensor. If you print at sizes different by the same ratio of the crop factor, you get exactly the same result as if you just took a full-frame photo, printed large, and then cropped out the middle.
Is the D3500 a crop sensor?
Nikon D3500 Specifications. … To start, the D3500’s 24 megapixel sensor is one of the best aps-c crop sensors on the market. Perhaps it’s even the best, though a number of other Nikon and Sony cameras have essentially the same sensor.



Discussion about this post