A “1 inch” sensor has about a 3x crop factor. The phrase “One Inch” makes them sound about the same size as a DSLR sensor, since real DSLR sensors are either about an inch wide (crop-frame) or an inch tall (full-frame) — but nothing about a 1″ sensor is anywhere near an inch or the size of a real DSLR sensor!
Also, What size is a 1/2.3 sensor?
Standard point-and-shoot cameras such as the Canon PowerShot SX280 HS and the Samsung Galaxy Camera use 1/2.3-inch sensors (6.17mm by 4.55 mm), while better ones such as the Nikon P7700 have a larger 1/1.7-inch (7.44mm by 5.58 mm) sensor.
Beside above What is a Type 1 sensor? The name of a 1″ digital sensor should more accurately be read as “one inch video camera tube equivalent” sensor. Current digital image sensor size descriptors are the video camera tube equivalency size, not the actual size of the sensor. For example, a 1″ sensor has a diagonal measurement of 16 mm.
Does sensor size really matter?
Right off the bat, let’s clear things up by saying yes, all things being equal, a larger sensor will give you a better image file, but like most matters in life, all things are not equal. The common wisdom is that for each jump in sensor size, you gain about a stop of performance in terms of noise and dynamic range.
What does 1 2.3 sensor mean?
1/2.3″ is exactly the same: it means 1″ divided by 2.3 (0.4347″ or 11.04mm).
Which phone camera sensor is best?
05. Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra. If we’re talking about hardware alone, then the Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra has everything it takes to be the best camera phone on our list. It’s got the largest camera sensor ever seen on a smartphone, creeping up to the 1-inch sensor size seen on pro-grade compact cameras.
Is CMOS sensor good?
CMOS sensors traditionally have lower quality, lower resolution and lower sensitivity. CMOS sensors are just now improving to the point where they reach near parity with CCD devices in some applications. CMOS cameras are usually less expensive and have great battery life.
How sensor size affect image quality?
The larger your camera’s sensor, the larger the photosites, the more resultant megapixels, which allow for a better image and a higher resolution. High resolution is important to ensure that your images are high quality even when you blow up a photo to a larger size.
Why is a bigger sensor better?
Larger Camera Sensors Have Better Image Quality
Larger camera sensors capture images with more light, less noise, more detail, and more of that beautiful background blur, to name a few. When comparing two cameras, if one has a larger sensor, that one will have better image quality.
Which camera sensor is best CMOS or CCD?
CMOS Sensors Are a Good Fit for Machine Vision
CMOS cameras can have higher framerates than their CCD counterparts. This is because the reading of the pixels can be done faster than having to wait for a CCD’s charge transfer.
Does sensor size affect image quality?
The larger your camera’s sensor, the larger the photosites, the more resultant megapixels, which allow for a better image and a higher resolution. High resolution is important to ensure that your images are high quality even when you blow up a photo to a larger size.
How do you calculate sensor size?
Sensor size refers to the physical size of the sensor, and is typically not noted on specification sheets. The best way to determine sensor size is to look at the pixel size on the sensor and multiply by the resolution.
What is the largest camera sensor?
Sharp just announced the Aquos R6 in Japan, and its Leica-branded lens sits in front of what is now the largest camera sensor on any phone. The 20-megapixel 1-inch sensor is similar in specs to what you’d find in Sony’s high-end RX100 compact cameras.
Why is CMOS better?
The advantages of CMOS sensors, however, outweigh the added complexity of the individual pixels. CMOS sensors are faster than their CCD counterparts, which allows for higher video frame rates. CMOS imagers provide higher dynamic range and require less current and voltage to operate.
How do CMOS sensors work?
Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)
In a CMOS sensor, the charge from the photosensitive pixel is converted to a voltage at the pixel site and the signal is multiplexed by row and column to multiple on chip digital-to-analog converters (DACs). Inherent to its design, CMOS is a digital device.
Which Sony IMX sensor is best?
Sony’s quad-pixel camera sensors are quite popular on smartphones. The 48MP Sony IMX586 was a raging success, thanks to its impact on mid-range photography.
…
Here are a few options that employ the sensor.
- Xiaomi Mi 10T 5G. …
- Samsung Galaxy M51. …
- Poco X3. …
- Realme 7 Pro. …
- Realme 7. …
- Samsung Galaxy M31s.
Who makes the best camera sensor?
The 10 best camera sensors on the market will surprise you
- Hasselblad X1D-50c (102)
- Pentax 645Z (101)
- Panasonic S1R (100)
- Nikon D850 (100)
- Sony A7R III (100)
- Nikon Z7 II (100)
- Sony A7R IV (99)
- Nikon Z7 (99)
Are larger sensors better in low light?
From physics point view, sensor size actually is irrelevant in low light performance. In the low light situation, the performance is dominated by lens which is independent of sensor. The bigger the lens, the more light it gets, the better IQ.
Which phone has the best camera sensor?
05. Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra. If we’re talking about hardware alone, then the Xiaomi Mi 11 Ultra has everything it takes to be the best camera phone on our list. It’s got the largest camera sensor ever seen on a smartphone, creeping up to the 1-inch sensor size seen on pro-grade compact cameras.
What cameras have CCD sensors?
CCD Still Has Advantages
When you do find one, it’s usually at the very high end of the premium point-and-shoot market–Canon’s PowerShot G12, Nikon’s Coolpix P7100, Olympus’s XZ-1, and Panasonic’s Lumix LX5, for example–where the potential user is primarily interested in still-image quality.
What is a CMOS sensor type?
Like CCDs, CMOS(Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor) sensors are semiconductor image sensors that convert light into electrical signals. CMOS sensors are semiconductor light sensors like CCDs.
How do you calculate sensor crop?
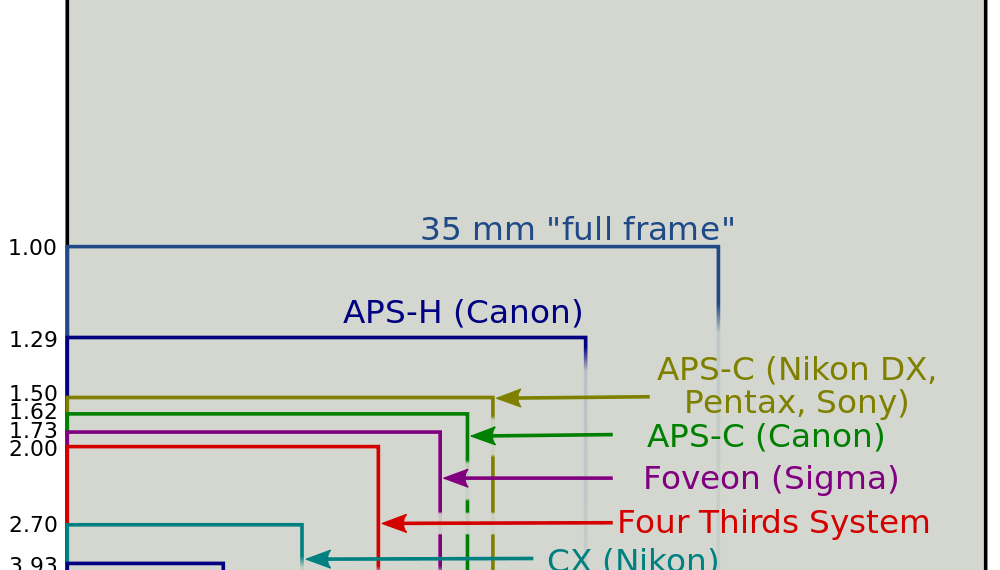
You take the provided crop factor number, multiply it with the focal length of the lens and you get the equivalent focal length relative to 35mm film / full-frame. For example, Nikon’s “DX” cameras have a crop factor of 1.5x, so if you take a 24mm wide-angle lens and multiply it by this number, the result is 36mm.
What is camera sensor size?
The size of sensor that a camera has ultimately determines how much light it uses to create an image. … For example, a Full Frame camera with 36 megapixels would have very similar sized pixels to an APS-C camera with 16 megapixels.
What size is a full frame sensor?
A full frame digital sensor refers to to the negative size of a 35mm film camera. These dimensions are 36mm x 24mm. This gives the aspect ratio of 3:2 (three units wide compared to two units tall), which is the ratio most DSLR cameras shoot in. By definition, a crop sensor is anything smaller than these measurements.



Discussion about this post